Integrating ERP with CRM and other business applications for seamless workflow is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a business imperative. Imagine a world where sales data instantly updates inventory levels, marketing campaigns automatically target high-potential leads, and customer service reps have immediate access to complete order history. This isn’t science fiction – it’s the reality enabled by a well-integrated system, boosting efficiency and driving revenue growth.
This article dives deep into the strategies, technologies, and considerations for achieving this streamlined, data-driven utopia.
From understanding the characteristics of a truly seamless workflow to navigating the complexities of data integration and security, we’ll cover everything you need to know. We’ll explore various integration methods, compare the costs and benefits, and showcase real-world examples of companies that have successfully implemented integrated systems. We’ll also address the critical aspects of user adoption and training, ensuring a smooth transition for your team.
Get ready to unlock the power of interconnected business applications!
Defining Seamless Workflow in Business Applications
Imagine a business where sales data automatically updates inventory levels, customer service reps instantly access order history, and marketing campaigns are fueled by real-time insights from sales performance. That’s the promise of a truly seamless workflow – a harmonious integration of different business applications that eliminates data silos and streamlines operations. This synergy allows for faster decision-making, improved efficiency, and ultimately, increased profitability.A seamless workflow between ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning), CRM (Customer Relationship Management), and other business applications is characterized by real-time data synchronization, automated processes, and a unified user experience.
Data flows effortlessly between systems, eliminating the need for manual data entry and reducing the risk of errors. Employees can access all relevant information from a single interface, regardless of the application it originates from. This integrated approach fosters better collaboration and transparency across different departments.
Workflow Bottlenecks in Integrated Systems
Despite the benefits of integration, challenges remain. Common workflow bottlenecks often arise from poorly designed integrations, incomplete data migration, or a lack of standardization across systems. These issues can manifest in several ways. For example, inconsistent data formats can lead to errors in reporting and analysis. Lack of proper data mapping between systems can cause delays in processing orders or responding to customer inquiries.
Furthermore, insufficient training for employees on the integrated system can result in slow adoption and continued reliance on older, less efficient methods. A lack of clear communication and collaboration between IT and business departments can also lead to integration projects falling short of expectations.
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for Workflow Efficiency
Measuring the success of a seamless workflow integration requires the right KPIs. These metrics should focus on efficiency gains, error reduction, and improved customer satisfaction. Some critical KPIs include:
- Order-to-cash cycle time: This measures the time it takes from order placement to payment receipt. A reduction indicates improved efficiency.
- Customer response time: This reflects how quickly customer inquiries are addressed. Faster response times translate to better customer satisfaction.
- Data entry errors: Tracking the number of data entry errors highlights the effectiveness of automated processes and data integration.
- Inventory accuracy: This measures the difference between recorded and actual inventory levels. High accuracy reflects the effectiveness of real-time inventory updates.
- Employee productivity: Tracking employee time spent on tasks related to data entry, reconciliation, and manual processes reveals areas for improvement. A decrease indicates increased productivity.
These KPIs provide quantifiable data to assess the effectiveness of the integrated system and identify areas needing further optimization. By continuously monitoring these metrics, businesses can ensure their integrated systems are delivering the promised efficiency and contributing to overall business growth.
Benefits of Integrating ERP and CRM
Integrating Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems offers significant advantages, streamlining business processes and boosting overall efficiency. By connecting these previously siloed systems, companies gain a unified view of their operations, improving data accuracy and enabling better decision-making across all departments. This integration leads to enhanced customer experiences, increased sales, and improved profitability.The synergy between ERP and CRM creates a powerful engine for growth.
Information flows seamlessly between departments, eliminating data duplication and inconsistencies. This unified data source provides a 360-degree view of each customer, enabling personalized interactions and targeted marketing campaigns. The resulting improvements in efficiency and customer satisfaction translate directly to increased revenue and reduced operational costs.
Improved Sales Performance
Integrated ERP and CRM systems provide sales teams with real-time access to critical customer data, including purchase history, past interactions, and current projects. This allows sales representatives to personalize their interactions, anticipate customer needs, and proactively address potential issues. For instance, if a customer’s order history shows a preference for a specific product line, the sales team can tailor their approach to highlight those products, increasing the likelihood of a successful sale.
Get the entire information you require about impact of cloud-based ERP on business agility and operational efficiency on this page.
Access to inventory levels through the ERP system also prevents overselling and ensures timely order fulfillment, enhancing customer satisfaction and building loyalty.
Enhanced Marketing Effectiveness
By combining CRM data on customer preferences and behavior with ERP data on sales trends and inventory levels, marketing teams can develop more targeted and effective campaigns. They can segment customers based on demographics, purchase history, and engagement levels, ensuring that marketing messages resonate with specific audiences. This precision marketing approach leads to higher conversion rates and a better return on investment (ROI) for marketing initiatives.
For example, a company could target customers who haven’t purchased in a while with a personalized offer based on their past purchases, encouraging repeat business.
Streamlined Customer Service Operations
Customer service representatives gain a comprehensive view of each customer’s interaction history through the integrated system. This enables them to quickly resolve issues, answer questions accurately, and provide personalized support. Access to order details, payment information, and past service requests within the CRM system allows for efficient troubleshooting and faster resolution times. This improved responsiveness leads to increased customer satisfaction and reduces the volume of support tickets, freeing up customer service resources to focus on more complex issues.
Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains
Maintaining separate ERP and CRM systems often leads to redundant data entry, increased IT costs, and reduced efficiency. Integration eliminates these inefficiencies by centralizing data and streamlining workflows. The reduction in manual data entry saves time and resources, while the improved data accuracy minimizes errors and reduces the need for costly corrections. A unified system also simplifies reporting and analysis, providing valuable insights into business performance.
For example, a company might save thousands of dollars annually by reducing the need for multiple software licenses and minimizing data entry errors.
Hypothetical Case Study: ROI of ERP and CRM Integration
Let’s consider a hypothetical mid-sized company, “Acme Corp,” with annual sales of $10 million. Before integration, Acme Corp maintained separate ERP and CRM systems, resulting in data inconsistencies, manual data entry, and inefficient workflows. They experienced an average of 10% lost sales due to inaccurate inventory information and an average customer service resolution time of 48 hours. After integrating their ERP and CRM systems, Acme Corp saw a 5% increase in sales due to improved sales efficiency and targeted marketing, resulting in an additional $500,000 in revenue.
They also reduced customer service resolution time to 24 hours, improving customer satisfaction and reducing operational costs. The cost of integration was $50,
Therefore, the ROI for Acme Corp is calculated as follows:
ROI = (Increased Revenue – Integration Cost) / Integration Cost = ($500,000 – $50,000) / $50,000 = 9
This represents a 900% return on investment within a short period, highlighting the significant financial benefits of ERP and CRM integration. This is just a hypothetical example; actual ROI will vary depending on the specific circumstances of each company.
Technical Aspects of Integration
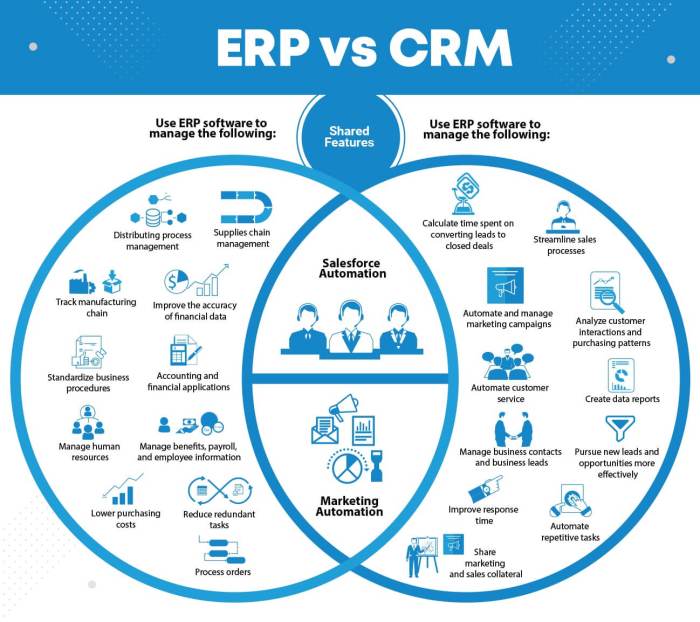
Integrating ERP and CRM systems, along with other business applications, requires a deep understanding of various technical approaches. The choice of integration method significantly impacts cost, complexity, and scalability. Selecting the right method is crucial for a seamless workflow and successful digital transformation. This section dives into the technical details of different integration methods and provides a framework for making informed decisions.
Several methods exist for integrating business applications, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. The ideal approach depends on factors like the complexity of the systems involved, the volume of data being exchanged, budget constraints, and the desired level of real-time integration. Understanding these nuances is key to a successful integration project.
Integration Methods: API, Middleware, and ETL
Three primary methods facilitate the integration of ERP, CRM, and other business applications: Application Programming Interfaces (APIs), middleware, and Extract, Transform, Load (ETL) processes. Each offers a distinct approach to data exchange and system interaction.
| Method | Cost | Complexity | Scalability |
|---|---|---|---|
| API Integration | Moderate to High (depending on customization) | Moderate to High (requires coding expertise) | High (easily adaptable to growing data volumes) |
| Middleware Integration | High (includes software licensing and maintenance) | High (requires specialized knowledge and configuration) | High (can handle complex integrations and large data sets) |
| ETL Integration | Moderate to High (depending on the tool and data volume) | Moderate (relatively simpler than API or middleware) | Moderate (can be scaled but might require adjustments for very large data volumes) |
Choosing the Right Integration Approach
Selecting the appropriate integration method requires a systematic approach. Consider the following steps:
- Assess your business needs: Define the specific data that needs to be exchanged between systems and the frequency of data transfer. For instance, real-time order updates require a different approach than batch processing of monthly sales data.
- Evaluate system capabilities: Determine the APIs and integration functionalities offered by your ERP, CRM, and other applications. Some systems might have built-in integration tools, while others may require custom development.
- Analyze budget and resources: API integration might be cost-effective for simpler scenarios, while middleware or ETL solutions might be necessary for complex integrations or large data volumes. Factor in the costs of software licenses, development, and ongoing maintenance.
- Consider scalability: Choose a method that can accommodate future growth and changes in your business processes. Cloud-based solutions often offer better scalability than on-premise solutions.
- Select the integration method: Based on the above considerations, choose the most suitable method. For example, a small business with limited resources might opt for ETL for periodic data synchronization, while a large enterprise might utilize middleware for real-time integration of multiple systems.
Data Management and Security Considerations
Integrating ERP and CRM systems, along with other business applications, creates a powerful, unified workflow. However, this interconnectedness also presents significant challenges in managing data and ensuring its security. A robust strategy is crucial to avoid data silos, inconsistencies, and potential breaches. The following sections detail the critical considerations for a secure and efficient integrated system.
Data synchronization across multiple systems is a major hurdle. Inconsistent data formats, differing update frequencies, and the sheer volume of information exchanged can lead to discrepancies and errors. Maintaining data consistency requires careful planning and the implementation of robust data governance policies. Security, too, is paramount. Protecting sensitive customer and business data requires a multi-layered approach that considers both technical and procedural safeguards.
Compliance with regulations like GDPR and CCPA is also essential.
Data Synchronization and Consistency
Effective data synchronization hinges on choosing the right integration method. Real-time integration offers immediate data updates but demands higher system performance and more complex configuration. Batch processing, on the other hand, offers greater flexibility and control but may introduce delays. Regardless of the method, data cleansing and transformation are crucial. This involves standardizing data formats, resolving inconsistencies, and removing duplicates before integration.
Regular data quality checks and reconciliation processes are also necessary to identify and address any discrepancies that may arise after integration.
Data Security and Compliance Best Practices
Protecting sensitive data in an integrated environment requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes implementing strong access controls, encrypting data both in transit and at rest, and regularly auditing system logs for suspicious activity. Choosing secure integration protocols, like HTTPS, is crucial, and rigorous security testing should be performed before and after integration. Furthermore, adhering to relevant data privacy regulations like GDPR and CCPA is non-negotiable.
This involves establishing clear data retention policies, providing users with control over their data, and implementing robust data breach response plans.
Security Measures Checklist
A comprehensive security checklist is essential to mitigate risks. This checklist should be reviewed and updated regularly to reflect evolving threats and best practices. The checklist should include items like:
- Data Encryption: Implement encryption both in transit and at rest for all sensitive data.
- Access Control: Implement role-based access control (RBAC) to limit access to sensitive data based on user roles and responsibilities.
- Regular Security Audits: Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing to identify vulnerabilities and ensure compliance.
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP): Implement DLP measures to prevent sensitive data from leaving the organization’s control.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploy IDPS to monitor network traffic and detect and prevent malicious activity.
- Incident Response Plan: Develop and regularly test an incident response plan to address data breaches and other security incidents.
- Employee Training: Provide regular security awareness training to employees to educate them on best practices and potential threats.
- Regular Software Updates: Keep all software and systems up-to-date with the latest security patches.
- Compliance Monitoring: Regularly monitor compliance with relevant data privacy regulations such as GDPR and CCPA.
User Adoption and Training: Integrating ERP With CRM And Other Business Applications For Seamless Workflow

Successfully integrating ERP and CRM systems hinges not just on technical prowess, but also on widespread user adoption. A well-designed training program and proactive change management are crucial for minimizing disruption and maximizing the return on investment. Ignoring these aspects can lead to underutilized systems and frustrated employees, ultimately undermining the entire integration effort.Effective user adoption requires a multi-pronged approach, combining comprehensive training with ongoing support and a culture that embraces change.
This involves understanding user needs, tailoring training materials accordingly, and fostering a collaborative environment where employees feel empowered to utilize the new system.
Strategies for Successful User Adoption
A successful integration requires a carefully planned strategy for user adoption. This involves more than just providing training; it necessitates a holistic approach that addresses potential resistance to change and fosters a positive attitude towards the new system. Key strategies include clear communication of the benefits, providing adequate support, and recognizing and rewarding early adopters. For instance, showcasing how the integrated system streamlines daily tasks and reduces workload can significantly improve buy-in.
Similarly, establishing a dedicated support team to address user queries and concerns promptly can prevent frustration and improve user experience. Incentivizing early adoption through rewards or recognition can also encourage colleagues to actively participate in the transition.
Designing an Effective Training Program
The training program should be modular, catering to different user roles and skill levels. Instead of a single, overwhelming session, break the training into manageable modules focusing on specific functionalities relevant to each role. For example, sales representatives might focus on CRM features, while accounting staff would concentrate on ERP modules. Hands-on exercises and real-world scenarios are crucial for effective learning.
The use of interactive simulations and role-playing can help employees understand the practical applications of the integrated system. Finally, post-training assessments and follow-up sessions ensure knowledge retention and address any lingering questions or challenges.
Best Practices for Change Management
Change management is paramount for minimizing disruption during the integration process. This involves open communication, active participation from key stakeholders, and a phased implementation approach. Regular updates and feedback sessions throughout the integration process keep employees informed and involved. Addressing concerns and providing solutions proactively can mitigate resistance. A phased rollout allows for iterative adjustments, minimizing the impact of unforeseen issues.
For example, starting with a pilot program in a specific department before a full-scale deployment allows for identification and resolution of any problems before impacting the entire organization. Furthermore, assigning dedicated change champions within each department can foster a supportive environment and facilitate the adoption process.
Choosing the Right Integration Partners and Tools
Integrating your ERP, CRM, and other business applications requires careful selection of integration partners and tools. The right choices can streamline operations and boost efficiency, while the wrong ones can lead to costly delays and integration headaches. This section Artikels key considerations for making informed decisions.Choosing the right integration partner and tools is crucial for a successful ERP-CRM integration.
The wrong choice can lead to project delays, budget overruns, and ultimately, a system that doesn’t meet your business needs. This involves careful evaluation of various factors, including vendor capabilities, cost-effectiveness, and long-term support.
Criteria for Selecting Integration Partners and Tools
Several key criteria should guide your selection process. These criteria ensure that the chosen partner and tools align with your business requirements and offer the necessary functionality and support. Consider factors such as the partner’s experience, their technical expertise, their pricing model, and their commitment to ongoing support and maintenance. A thorough evaluation will minimize risks and maximize the return on investment.
- Experience and Expertise: Look for partners with a proven track record of successful ERP-CRM integrations, particularly within your industry. Their experience should encompass various integration methods and technologies.
- Technical Capabilities: Assess their proficiency in relevant technologies such as APIs, ETL tools, and middleware. They should demonstrate a deep understanding of your specific ERP and CRM systems.
- Pricing and Contract Terms: Clearly understand the pricing model (hourly rates, fixed fees, etc.) and contract terms. Avoid hidden costs and ensure transparency in pricing.
- Support and Maintenance: A reliable partner offers robust support and maintenance services, including timely issue resolution and proactive system monitoring.
- Scalability and Flexibility: Choose tools and partners that can adapt to your evolving business needs and scale as your company grows.
Comparison of Vendor Offerings, Integrating ERP with CRM and other business applications for seamless workflow
Different vendors offer a variety of integration solutions, each with its own strengths and weaknesses. For example, some vendors might specialize in cloud-based integrations, while others might focus on on-premise solutions. Consider factors like ease of use, customization options, and the vendor’s overall reputation when comparing offerings. It’s important to request demos and conduct thorough testing before making a final decision.For instance, Vendor A might offer a highly customizable but expensive solution with excellent support, while Vendor B might provide a more affordable, off-the-shelf solution with limited customization options and less robust support.
The optimal choice depends on your specific needs and budget.
Decision Matrix for Evaluating Integration Partners
A decision matrix can help you objectively compare different vendors. The following table provides a framework for evaluating potential integration partners based on key criteria. Remember to adjust the weighting of each criterion based on your specific priorities.
| Vendor | Cost (Weight: 2) | Experience (Weight: 3) | Support (Weight: 2) | Total Weighted Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Vendor A | 7 | 9 | 8 | 37 |
| Vendor B | 9 | 7 | 6 | 32 |
| Vendor C | 6 | 8 | 7 | 33 |
Note: Scores are hypothetical and range from 1 (poor) to 10 (excellent). Weights reflect the relative importance of each criterion. For example, experience might be considered more important than cost in some scenarios. The total weighted score helps to rank vendors based on your priorities.
Case Studies of Successful ERP/CRM Integrations
Integrating Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Customer Relationship Management (CRM) systems can dramatically improve a business’s efficiency and profitability. However, successful integration requires careful planning and execution. The following case studies illustrate the potential benefits and highlight the challenges that organizations have overcome.
Case Study 1: Manufacturing Giant Streamlines Operations
A large multinational manufacturing company, with over 10,000 employees and operations across several continents, faced significant challenges managing its customer data, inventory, and production processes. Their disparate systems led to data silos, inaccurate forecasting, and inefficient communication between departments. To address these issues, they implemented a comprehensive ERP/CRM integration project using a cloud-based solution. The integration linked their existing ERP system with a new CRM platform, enabling real-time data synchronization across sales, marketing, production, and customer service.The integration approach involved a phased rollout, starting with a pilot program in a single region.
This allowed the company to identify and resolve potential issues before expanding the integration to other regions. A significant challenge was data migration – ensuring data accuracy and consistency across the disparate systems. The company overcame this by implementing robust data cleansing and validation processes.
- Challenge: Disparate systems leading to data silos and inefficiencies.
- Solution: Cloud-based ERP/CRM integration with phased rollout.
- Outcome: Improved forecasting accuracy, reduced inventory costs, enhanced customer service, and increased sales.
Case Study 2: Retailer Enhances Customer Experience
A mid-sized retail chain with over 50 stores across a national market struggled with inconsistent customer data across its various channels (online, in-store, phone). This lack of a unified customer view hampered personalized marketing efforts and customer service responsiveness. They chose to integrate their existing ERP system with a new, more robust CRM system, focusing on a unified customer profile.
The integration project involved significant data cleansing and standardization, mapping data fields between the two systems to ensure consistency. A key challenge was integrating data from various sources, including point-of-sale systems, e-commerce platforms, and loyalty programs.The company employed a hybrid integration approach, using both APIs and ETL (Extract, Transform, Load) processes. This allowed them to integrate data from different sources in a flexible and efficient manner.
Training employees on the new integrated system was also a critical aspect of the project’s success.
- Challenge: Inconsistent customer data across channels.
- Solution: Hybrid integration approach using APIs and ETL processes, with a focus on a unified customer profile.
- Outcome: Improved customer experience, targeted marketing campaigns, increased customer loyalty, and higher sales conversion rates.
Case Study 3: Service Provider Improves Operational Efficiency
A large service provider with a geographically dispersed workforce needed to improve the efficiency of its service delivery and project management. Their existing systems were fragmented, making it difficult to track project progress, manage resources, and communicate effectively with clients. The company implemented a tightly integrated ERP/CRM solution, allowing project managers to access real-time data on resource availability, project timelines, and customer interactions.
A significant challenge was integrating legacy systems with the new platform. This required careful planning and the development of custom integration solutions.The integration approach involved a combination of custom development and pre-built connectors. The company also invested heavily in employee training to ensure smooth user adoption.
- Challenge: Fragmented systems hindering efficient service delivery and project management.
- Solution: Tightly integrated ERP/CRM solution with custom development and pre-built connectors.
- Outcome: Improved project management, enhanced resource allocation, increased customer satisfaction, and reduced operational costs.
Future Trends in ERP/CRM Integration

The convergence of ERP and CRM systems is rapidly evolving, driven by advancements in technology and the ever-increasing need for businesses to operate with agility and efficiency. The future of integrated business applications promises seamless data flow, enhanced decision-making, and a more customer-centric approach. This section explores the key technological drivers shaping this future and the opportunities and challenges they present.
Emerging technologies are fundamentally reshaping the landscape of ERP/CRM integration, creating both exciting possibilities and significant hurdles for businesses. The successful navigation of these changes will depend on strategic planning, investment in the right technologies, and a commitment to upskilling the workforce.
The Impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI)
AI is poised to revolutionize ERP/CRM integration by automating complex tasks, improving data analysis, and personalizing customer interactions. AI-powered chatbots can handle routine customer inquiries, freeing up human agents to focus on more complex issues. Predictive analytics, driven by AI algorithms, can analyze vast datasets from integrated ERP and CRM systems to forecast sales trends, optimize inventory management, and identify potential risks.
For instance, a retail company could leverage AI to predict customer churn based on purchase history and CRM interactions, enabling proactive interventions to retain valuable customers. This proactive approach leads to better customer retention and improved revenue.
Cloud Computing’s Expanding Role
Cloud computing is a cornerstone of modern ERP/CRM integration, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost-effectiveness. Cloud-based solutions enable businesses to access and share data from anywhere, anytime, fostering real-time collaboration and improved decision-making. The shift towards cloud-based systems allows for easier updates and integration of new technologies, reducing the burden on IT infrastructure and facilitating faster deployment of new functionalities.
Companies like Salesforce, with its cloud-based CRM, exemplify this trend, offering seamless integration with various ERP systems through APIs and pre-built connectors.
Blockchain’s Potential for Enhanced Security and Transparency
Blockchain technology, known for its secure and transparent nature, offers significant potential for enhancing data security and traceability in integrated ERP/CRM systems. Blockchain can be used to create immutable records of transactions, ensuring data integrity and preventing unauthorized modifications. This is particularly beneficial in industries with stringent regulatory requirements, such as healthcare and finance. For example, a pharmaceutical company could utilize blockchain to track the movement of drugs throughout the supply chain, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeiting.
This increased transparency and security enhances trust among stakeholders.
Predicting the Future of Integrated Business Applications
The future of integrated business applications points towards a more holistic and intelligent approach to business operations. We can expect to see greater automation, improved data analysis, and a more personalized customer experience. The integration of IoT devices will further enhance data collection and analysis, leading to more accurate predictions and improved decision-making. The lines between ERP and CRM will continue to blur, with functionalities merging to create a unified platform that supports all aspects of the business.
For example, we might see a future where a single platform manages not only sales and customer data but also supply chain, manufacturing, and financial operations, creating a truly unified view of the business.
Challenges and Opportunities in Adapting to New Trends
The adoption of these new technologies presents both opportunities and challenges. Businesses will need to invest in infrastructure upgrades, employee training, and robust cybersecurity measures. Data migration can be complex and time-consuming, requiring careful planning and execution. However, the potential rewards are significant, including increased efficiency, improved customer satisfaction, and enhanced competitiveness. Companies that successfully navigate these challenges will be well-positioned to leverage the full potential of integrated ERP/CRM systems and gain a significant advantage in the marketplace.
The key to success will be a strategic approach that prioritizes data security, employee training, and a clear understanding of business needs.