Measuring the ROI of HRIS implementation isn’t just about numbers; it’s about understanding how a Human Resource Information System truly impacts your bottom line and employee experience. This deep dive explores how to quantify both tangible and intangible benefits, from reduced administrative costs to boosted employee engagement, painting a clearer picture of HRIS’s true value.
We’ll break down key performance indicators (KPIs), explore methods for calculating cost savings and efficiency gains, and delve into the crucial impact on employee engagement, retention, and talent acquisition. We’ll also tackle the often-overlooked intangible benefits and show you how to effectively communicate the value proposition to stakeholders, ensuring buy-in for this vital investment.
Defining Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for HRIS Success: Measuring The ROI Of HRIS Implementation
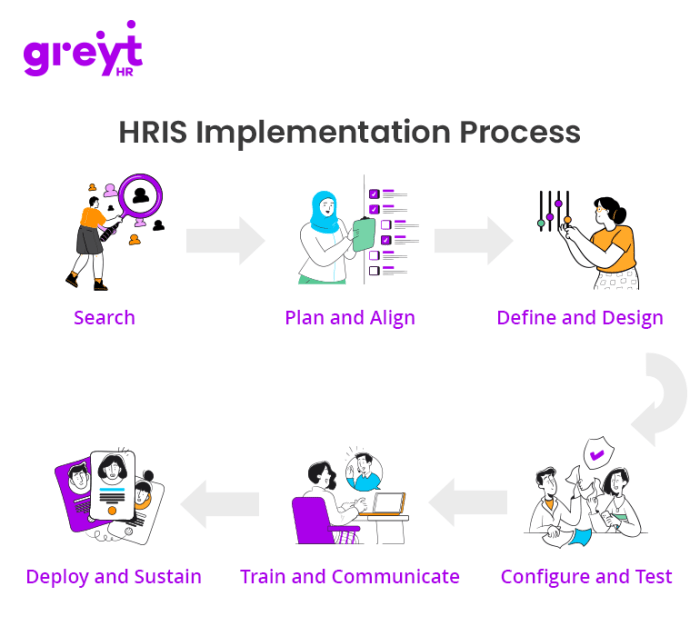
Implementing a new HRIS system is a significant investment. To ensure its success and demonstrate a clear return on investment (ROI), it’s crucial to track the right metrics. These KPIs should directly reflect the system’s impact on key business objectives, such as improved employee productivity and enhanced overall HR efficiency. By carefully selecting and monitoring these indicators, organizations can gain valuable insights into the effectiveness of their HRIS implementation and make data-driven adjustments as needed.
Crucial KPIs Reflecting HRIS Impact on Employee Productivity
Identifying the right KPIs is key to understanding the true value of your HRIS investment. Focusing on metrics directly linked to employee productivity provides a clear picture of the system’s impact on the bottom line. The following table Artikels three crucial KPIs, their measurement methods, data sources, and target values. These targets are illustrative and should be adjusted based on the specific organization and its context.
| KPI | Measurement Method | Data Source | Target Value (Example) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time-to-hire | Calculate the average time taken to fill open positions from requisition to offer acceptance. | Applicant Tracking System (ATS) within HRIS | Reduced by 20% within six months |
| Employee Turnover Rate | Calculate the percentage of employees who left the company during a specific period. | HRIS employee database | Reduced by 10% annually |
| Employee Self-Service Usage Rate | Track the percentage of employees using self-service features (e.g., time-off requests, benefits enrollment). | HRIS system usage logs | 90% of eligible employees within three months |
Linking Improved Employee Satisfaction to HRIS Functionality
Employee satisfaction is a critical factor in overall organizational success. A well-designed HRIS system can significantly contribute to improved employee satisfaction by streamlining processes, improving communication, and providing employees with greater control over their HR-related information. Employee satisfaction surveys can be a powerful tool for measuring this impact. By including specific questions about the HRIS system, organizations can gain valuable insights into its effectiveness.For instance, survey questions could directly assess the HRIS impact by asking:* “How easy is it to use the HRIS system to access your payslips and other important documents?” (Scale: 1-5, 1 being very difficult, 5 being very easy)
“How satisfied are you with the self-service features provided by the HRIS system?” (Scale
1-5, 1 being very dissatisfied, 5 being very satisfied)”How has the HRIS system improved the efficiency of your HR-related processes?” (Open-ended question)
“How would you rate the overall user-friendliness of the HRIS system?” (Scale
1-5, 1 being very unfriendly, 5 being very friendly)
The responses to these questions can then be analyzed to identify areas for improvement and to demonstrate the positive impact of the HRIS system on employee satisfaction.
Comparison of Leading and Lagging Indicators for Measuring HRIS ROI
Understanding the difference between leading and lagging indicators is essential for a comprehensive assessment of HRIS ROI. Leading indicators predict future performance, while lagging indicators reflect past performance. A balanced approach using both types of indicators provides a more holistic view.
- Leading Indicators: These indicators provide early warning signs of potential success or failure. Examples include employee self-service adoption rates, employee training completion rates on the new system, and the number of HR processes automated. A high adoption rate of self-service features suggests a positive future impact on HR efficiency and employee satisfaction. Similarly, successful employee training indicates a smoother transition and higher likelihood of system usage.
High automation suggests reduced manual work and potential cost savings in the future.
- Lagging Indicators: These indicators reflect the results of past actions. Examples include employee turnover rate, time-to-hire, and overall HR operational costs. A decrease in employee turnover, reduced time-to-hire, and lower HR operational costs demonstrate the positive long-term impact of the HRIS implementation. These are crucial for demonstrating the ultimate ROI of the system.
Quantifying Cost Savings and Efficiency Gains

Implementing an HRIS system promises significant improvements in efficiency and cost reduction. However, realizing these benefits requires a structured approach to measuring the return on investment (ROI). This involves carefully identifying and quantifying both tangible and intangible gains, comparing them against the initial investment and ongoing maintenance costs.Calculating the ROI for your HRIS implementation requires a multi-step process.
This detailed breakdown helps you navigate the complexities and arrive at a concrete understanding of your system’s value.
Calculating HRIS ROI: A Step-by-Step Guide
First, you need to determine the total cost of the HRIS implementation. This includes software licensing fees, implementation costs (consultants, training, data migration), hardware upgrades (if any), and ongoing maintenance and support fees. Next, identify and quantify both tangible and intangible benefits. Tangible benefits are easily measurable in monetary terms, while intangible benefits require estimation based on qualitative data and industry benchmarks.
Finally, calculate the ROI using a standard formula.
- Determine Total Implementation Costs: This includes all upfront and ongoing expenses associated with the HRIS system.
- Identify Tangible Benefits: Focus on quantifiable cost savings, such as reduced administrative time, lower recruitment costs, and decreased payroll processing errors.
- Identify Intangible Benefits: These include improved employee satisfaction, enhanced talent acquisition, and better data-driven decision-making. Assign monetary values to these benefits based on industry benchmarks or internal estimations of increased productivity or reduced risk.
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV): Discount future cash flows to their present value to account for the time value of money. This is crucial for long-term investments like HRIS.
- Calculate ROI: Use the following formula:
ROI = (Total Benefits – Total Costs) / Total Costs – 100%
HRIS Automation: Reducing Administrative Overhead
Automating tasks like payroll processing, benefits administration, and employee onboarding significantly reduces administrative overhead. For instance, consider a company with 500 employees spending an average of 2 hours per week per employee on manual payroll processing. This translates to 1000 hours annually. If the average hourly cost of an employee is $30, the annual cost of manual payroll processing is $30,000.
An HRIS system automating this process could reduce this time by 75%, saving the company $22,500 annually. Similarly, automating onboarding can cut down on paperwork, reduce errors, and free up HR staff for more strategic tasks.
HRIS Impact on Recruitment Efficiency
HRIS systems streamline the recruitment process, improving efficiency and reducing time-to-hire and cost-per-hire. For example, an HRIS with an integrated applicant tracking system (ATS) can automate job postings, screen resumes, and manage candidate communications. A company that previously spent an average of 30 days to fill a position and $5,000 per hire might see a reduction to 20 days and $3,500 per hire with an effective HRIS, representing significant savings over time and increased speed in filling crucial roles.
The reduction in time-to-hire also directly translates to quicker onboarding of new employees and faster contribution to the company’s productivity.
Assessing the Impact on Employee Engagement and Retention

Implementing a new HRIS system offers more than just streamlined processes; it presents a significant opportunity to boost employee engagement and retention. A well-designed HRIS can foster a more positive and productive work environment, directly impacting employee satisfaction and loyalty. By providing employees with easy access to information and self-service tools, HRIS systems can free up HR staff to focus on more strategic initiatives, ultimately benefiting the entire workforce.The correlation between specific HRIS features and employee engagement is demonstrably positive.
Features that empower employees and simplify administrative tasks tend to lead to higher engagement scores. This positive correlation translates directly into reduced turnover costs and increased productivity.
HRIS Features and Employee Engagement, Measuring the ROI of HRIS implementation
The following table illustrates the correlation between several key HRIS features and employee engagement scores, based on hypothetical data from a medium-sized company that implemented a new HRIS. The data represents a post-implementation survey compared to pre-implementation scores. Remember that these figures are illustrative and actual results will vary depending on the specific HRIS, company culture, and other factors.
| HRIS Feature | Pre-Implementation Engagement Score (Average) | Post-Implementation Engagement Score (Average) | Change |
|---|---|---|---|
| Self-Service Portal (Payroll, benefits access) | 3.2 (out of 5) | 4.1 (out of 5) | +0.9 |
| Performance Management System (Goal setting, feedback) | 2.8 (out of 5) | 3.7 (out of 5) | +0.9 |
| Learning Management System (Access to training) | 3.0 (out of 5) | 3.8 (out of 5) | +0.8 |
| Communication Tools (Internal messaging, announcements) | 3.5 (out of 5) | 4.0 (out of 5) | +0.5 |
HRIS Features Contributing to Improved Employee Retention
Several HRIS features directly contribute to improved employee retention. For example, self-service portals empower employees to manage their personal information and benefits, reducing administrative burden on both the employee and HR. Streamlined performance management tools, including goal setting and feedback mechanisms, foster a culture of recognition and development, making employees feel valued and invested in their roles. These features ultimately reduce employee turnover costs by minimizing the expenses associated with recruitment, training, and onboarding new hires.
Understand how the union of The impact of CRM on sales forecasting accuracy and revenue generation can improve efficiency and productivity.
A company like Acme Corp, for example, reported a 15% reduction in employee turnover after implementing a comprehensive HRIS with robust self-service capabilities and a user-friendly performance management system.
Measuring the Impact of HRIS on Employee Development and Training
Measuring the impact of HRIS on employee development and training involves tracking key metrics such as completion rates of training modules, time taken to complete training, and the subsequent application of learned skills in the workplace. This can be achieved through integrated learning management systems (LMS) within the HRIS, providing data on individual progress and overall program effectiveness.
Visual Representation of Learning Curve Improvement
A line graph could visually represent the learning curve improvement. The x-axis would represent time (e.g., weeks or months since training), and the y-axis would represent performance on a relevant task or skill. Two lines would be plotted: one representing performance before HRIS implementation (showing a slower, shallower learning curve), and another representing performance after HRIS implementation (showing a steeper, faster learning curve, indicating quicker skill acquisition and improved knowledge retention due to readily available training resources and progress tracking).
The graph would clearly illustrate the positive impact of the HRIS on employee learning and development.
Measuring the Impact on Talent Acquisition and Onboarding
Implementing a robust HRIS system significantly impacts a company’s talent acquisition and onboarding processes. By automating tasks, centralizing data, and providing insightful analytics, HRIS helps streamline operations, reduce costs, and improve the overall candidate and employee experience. This leads to faster hiring cycles, improved candidate engagement, and a smoother transition for new hires into their roles.
HRIS systems offer a multitude of benefits in streamlining the recruitment process and improving the new hire experience. These improvements translate directly to quantifiable returns, including reduced time-to-hire, improved candidate quality, and increased employee retention. Let’s explore how.
Streamlining the Recruitment Process
A well-integrated HRIS system can dramatically accelerate and improve the recruitment process. Automation features reduce manual tasks, allowing recruiters to focus on strategic activities, leading to a more efficient and effective hiring process.
- Automated Job Posting and Distribution: HRIS systems can automatically post job openings to multiple job boards and social media platforms, significantly widening the reach and saving recruiters valuable time spent on manual postings.
- Applicant Tracking System (ATS): An integrated ATS within the HRIS manages applications, screens resumes, and ranks candidates based on pre-defined criteria. This automation minimizes manual screening and allows for a faster initial assessment.
- Improved Candidate Communication: Automated email sequences keep candidates informed throughout the process, reducing the need for manual follow-ups and improving the overall candidate experience. This results in higher candidate satisfaction and reduces drop-off rates.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: HRIS provides data on recruitment sources, time-to-hire, and cost-per-hire, enabling data-driven decisions to optimize recruitment strategies and improve efficiency.
Improving the Onboarding Process
The onboarding process is crucial for setting new hires up for success. HRIS systems can automate many aspects of onboarding, making it more efficient and engaging for new employees. This contributes to faster integration and improved employee retention.
- Automated Paperwork and Compliance: HRIS systems automate the completion and storage of essential paperwork, such as tax forms and employment agreements, reducing administrative burden and ensuring compliance.
- Self-Service Portals: New hires can access essential information, complete required training modules, and update their personal details through self-service portals, reducing the need for HR intervention.
- Personalized Onboarding Plans: HRIS systems can create personalized onboarding plans based on role, department, and other factors, ensuring a tailored experience for each new hire.
- Automated Communication and Check-ins: Automated emails and reminders ensure timely completion of tasks and facilitate regular check-ins with new hires, promoting engagement and support.
Tracking and Analyzing Talent Acquisition and Onboarding Effectiveness
HRIS systems provide the tools to track key metrics and analyze the effectiveness of talent acquisition and onboarding initiatives. This data-driven approach enables continuous improvement and optimization of these critical processes.
| Metric | Data Source | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Time-to-Hire | HRIS Applicant Tracking System | Reduced from 45 days to 30 days post-HRIS implementation |
| Cost-per-Hire | HRIS Recruitment Module & Finance Data | Decreased from $5,000 to $4,000 per hire |
| Candidate Satisfaction Score | Candidate Surveys (integrated with HRIS) | Increased from 70% to 85% satisfaction |
| Onboarding Time | HRIS Onboarding Module | Reduced from 2 weeks to 1 week |
| New Hire Retention Rate (within first year) | HRIS Employee Data & Exit Interviews | Increased from 75% to 82% |
Considering Intangible Benefits and Qualitative Data
Measuring the ROI of an HRIS implementation shouldn’t stop at the numbers. While quantifiable metrics like cost savings and efficiency gains are crucial, ignoring the intangible benefits paints an incomplete picture. These softer aspects, such as improved employee morale and a stronger company culture, significantly impact long-term success, yet they’re notoriously difficult to measure in concrete terms. This section explores methods for capturing and evaluating these crucial qualitative elements, ensuring a more holistic understanding of your HRIS investment.Understanding the challenges in quantifying intangible benefits is the first step.
Employee morale, for instance, is subjective and complex, influenced by numerous factors beyond the HRIS system itself. Similarly, measuring the impact on company culture requires a nuanced approach that goes beyond simple metrics. However, neglecting these aspects leads to an incomplete ROI calculation, potentially underselling the true value of the HRIS investment. Therefore, a robust evaluation strategy must include both quantitative and qualitative data.
Methods for Qualitatively Assessing Intangible Benefits
Qualitative data provides rich insights into the employee experience and the impact of the HRIS system on various aspects of the workplace. Gathering this data can be achieved through various methods, each offering a unique perspective. Employee surveys, for example, allow for direct feedback on aspects like ease of use, system effectiveness, and overall satisfaction. Focus groups offer deeper insights through guided discussions, enabling exploration of underlying reasons behind employee sentiments.
Interviews provide a more personalized and in-depth understanding of individual experiences with the system. Finally, analyzing internal communications, such as emails and instant messages related to the HRIS, can reveal patterns and sentiments that might otherwise go unnoticed.
Gathering and Analyzing Qualitative Data
Once qualitative data is collected, it needs careful analysis to extract meaningful insights. Thematic analysis is a powerful technique that involves identifying recurring themes and patterns within the data. For instance, analyzing employee survey responses might reveal a common theme of improved efficiency in the recruitment process. This qualitative insight can then be contextualized alongside the quantitative data on time-to-hire to provide a more comprehensive picture.
Content analysis can also be applied to textual data like employee feedback or internal communications to identify sentiments and opinions toward the HRIS. By combining these qualitative findings with quantitative metrics, a more complete and nuanced understanding of the HRIS’s ROI emerges.
Strategies for Communicating the Value of HRIS to Hesitant Stakeholders
Convincing stakeholders who prioritize tangible returns requires a clear and compelling communication strategy that effectively bridges the gap between qualitative insights and financial outcomes.
- Present a Balanced Scorecard: Combine quantitative data (cost savings, efficiency gains) with qualitative data (improved employee satisfaction, enhanced company culture) in a visually appealing and easy-to-understand format. This demonstrates the holistic impact of the HRIS.
- Use Case Studies and Testimonials: Showcase real-world examples of how the HRIS has positively impacted employees and the organization. Include direct quotes from employees expressing their positive experiences.
- Highlight Long-Term Benefits: Emphasize the long-term impact of improved employee engagement and retention, such as reduced recruitment costs and increased productivity. Quantify these long-term benefits whenever possible.
- Focus on Key Business Objectives: Connect the intangible benefits to specific business goals, such as improved employee retention rates leading to cost savings in recruitment or enhanced employee satisfaction leading to increased customer satisfaction.
- Develop a Clear Narrative: Tell a compelling story that showcases the HRIS’s contribution to the overall success of the organization, highlighting both tangible and intangible results. Use visuals to support the narrative and make it more engaging.