Strategies for improving sales team productivity using CRM data analytics is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s the key to unlocking exponential growth in today’s competitive market. This deep dive explores how leveraging the power of CRM data analytics can transform your sales team from good to great. We’ll uncover actionable strategies to identify top performers, pinpoint bottlenecks in your sales cycle, and refine your processes for maximum efficiency.
Get ready to revolutionize your sales approach!
From identifying key performance indicators (KPIs) and analyzing sales cycle stages to optimizing sales processes and enhancing team training, we’ll equip you with the knowledge and tools to harness the full potential of your CRM data. We’ll also delve into advanced techniques like sales forecasting and lead management, providing practical examples and clear, concise steps you can implement immediately to see tangible results.
Prepare to witness a significant boost in your team’s productivity and overall sales performance.
Identifying Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) from CRM Data
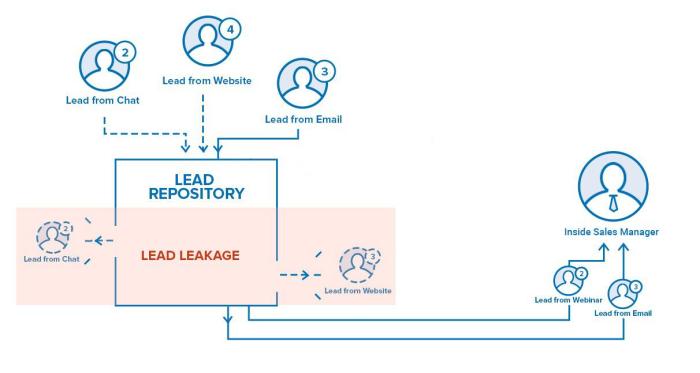
Unlocking the true potential of your sales team hinges on understanding their performance. CRM data provides a goldmine of insights, allowing you to identify areas for improvement and celebrate successes. By strategically analyzing this data, you can pinpoint exactly where your team excels and where it needs support, ultimately boosting overall productivity. This involves selecting the right Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) and effectively visualizing them.
Extracting actionable insights from your CRM requires focusing on the most impactful metrics. While numerous KPIs exist, prioritizing those directly reflecting sales team productivity is crucial. This allows for efficient analysis and targeted interventions to drive growth.
Three Crucial Sales KPIs
Three crucial sales KPIs directly extractable from CRM data to measure team productivity are: Average Deal Size, Conversion Rate, and Sales Cycle Length. Analyzing these metrics provides a comprehensive view of sales performance, highlighting areas needing improvement and celebrating team successes.
Visualizing KPIs Using a Responsive HTML Table, Strategies for improving sales team productivity using CRM data analytics
A clear visualization of these KPIs is essential for effective communication and action planning. The following table illustrates how to present this data in a readily understandable format. Note that the data presented is for illustrative purposes only.
| KPI | Current Performance | Target | Improvement Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average Deal Size | $5,000 | $7,500 | Implement upselling/cross-selling strategies; focus on higher-value clients. |
| Conversion Rate | 20% | 30% | Refine lead qualification process; improve sales pitch effectiveness; personalize follow-up communications. |
| Sales Cycle Length | 30 days | 20 days | Streamline sales processes; automate repetitive tasks; improve communication efficiency. |
Segmenting Sales Data to Identify High and Low Performers
Data segmentation allows for a granular understanding of individual representative performance. By analyzing each representative’s performance against the chosen KPIs (Average Deal Size, Conversion Rate, and Sales Cycle Length), you can easily identify high and low performers. For example, representatives consistently exceeding targets across all three KPIs can be considered high performers. Conversely, those consistently falling short across multiple KPIs might require additional training or support.
This segmentation allows for targeted coaching, resource allocation, and skill development initiatives, ultimately improving overall team productivity. This granular analysis ensures that support is directed where it is most needed, fostering a culture of continuous improvement and maximizing the potential of each team member.
Analyzing Sales Cycle Stages and Bottlenecks
Unlocking the secrets to improved sales team productivity often lies in understanding the intricacies of the sales cycle. By meticulously analyzing each stage, you can identify bottlenecks hindering progress and implement targeted strategies for optimization. This involves leveraging the power of your CRM data to gain actionable insights and boost overall sales performance.Analyzing the sales cycle length, broken down into its constituent stages, is crucial for pinpointing areas needing attention.
A well-defined sales cycle, tracked effectively within your CRM, allows for a comprehensive understanding of where deals are getting stuck and how long each step takes on average. This data-driven approach enables informed decision-making, leading to more efficient processes and increased revenue.
Sales Cycle Length Analysis: A Step-by-Step Procedure
To effectively analyze your sales cycle length, follow these steps:
- Define Sales Stages: Clearly define the stages in your sales process within your CRM. This might include Prospecting, Qualification, Presentation, Proposal, Negotiation, and Closing. Ensure consistency across your team.
- Track Time Spent in Each Stage: Configure your CRM to automatically track the time spent in each stage. This often involves setting custom fields or leveraging existing functionalities.
- Aggregate Data: Once sufficient data is collected, aggregate the data to calculate the average time spent in each stage across all deals.
- Identify Outliers: Look for deals that took significantly longer or shorter than average in specific stages. Investigate these outliers to understand the contributing factors.
- Analyze Trends: Analyze trends over time to see if the average time spent in any stage is increasing or decreasing. This will help identify emerging bottlenecks or improvements.
Common Sales Cycle Bottlenecks
Analyzing CRM data often reveals common bottlenecks. Understanding these bottlenecks is critical for implementing targeted improvements.
- Lead Qualification: Spending excessive time qualifying leads that ultimately don’t convert. Example: A lengthy qualification process involving multiple touchpoints without clear criteria may result in wasted time on unsuitable leads.
- Proposal Stage: Delays in creating and sending proposals, or slow response times from prospects. Example: A lack of standardized proposal templates or inefficient internal review processes can significantly prolong this stage.
- Negotiation Stage: Protracted negotiations due to unclear pricing strategies or a lack of negotiating skills. Example: Unclear pricing models or inconsistent messaging can lead to prolonged negotiations and potential deal loss.
- Closing Stage: Difficulty in securing final approvals or signatures. Example: Lack of follow-up or unclear next steps can cause deals to stall in the closing stage.
Visual Representation of Average Time Spent in Each Sales Cycle Stage
The following bullet points illustrate a hypothetical example of average time spent in each sales cycle stage. This visualization highlights potential areas for improvement. Remember to replace this example with your own data from your CRM.* Prospecting: 5 days
Qualification
3 days
Presentation
Browse the multiple elements of integrating ERP with CRM and other business applications for seamless workflow to gain a more broad understanding.
2 days
Proposal
7 days (Potential Bottleneck)*
Negotiation
4 days
Closing
2 days
Leveraging CRM Data to Improve Sales Forecasting: Strategies For Improving Sales Team Productivity Using CRM Data Analytics

Accurate sales forecasting is the cornerstone of a thriving business. It allows for strategic resource allocation, informed budget planning, and proactive adaptation to market fluctuations. By harnessing the power of CRM data, businesses can move beyond guesswork and build robust, data-driven sales predictions. This allows for a more precise understanding of future performance and empowers companies to make better, more informed decisions.CRM systems are treasure troves of valuable sales data.
This data, when properly analyzed, can reveal hidden patterns and trends that inform accurate sales forecasting. By leveraging historical sales data, such as past deal sizes, close rates, sales cycle lengths, and customer demographics, businesses can build predictive models that significantly improve their forecasting accuracy. This, in turn, leads to better resource management and more effective strategic planning.
Methods for Using Historical CRM Data to Predict Future Sales Performance
Several methods exist for using historical CRM data to predict future sales performance. These methods range from simple calculations based on past averages to sophisticated statistical modeling techniques. One common approach is to analyze historical sales data to identify trends and seasonality. For instance, a company might observe higher sales during the holiday season or a particular time of year.
This seasonal trend can then be incorporated into the forecasting model to adjust predictions accordingly. Another approach involves segmenting customers based on various factors, such as demographics, purchase history, or engagement levels, to identify high-value customer segments. Forecasts can then be tailored to each segment, resulting in more accurate predictions. Finally, advanced statistical methods, such as regression analysis or machine learning algorithms, can be applied to analyze complex relationships between different variables and build highly accurate predictive models.
Comparison of Two Forecasting Models
Two commonly used forecasting models are the moving average and exponential smoothing methods. The moving average method calculates the average sales over a specific period (e.g., the past three months). This average is then used as the forecast for the next period. While simple to implement, the moving average method can be slow to react to changes in sales trends.
Exponential smoothing, on the other hand, gives more weight to recent data points, making it more responsive to recent trends. It assigns exponentially decreasing weights to older data points, thus making it more sensitive to recent changes in sales patterns. For example, if sales suddenly spike, exponential smoothing will incorporate this spike more quickly into its forecast than the moving average method.
The choice between these models depends on the specific characteristics of the sales data and the desired level of responsiveness to recent trends. A company experiencing rapid growth might prefer exponential smoothing, while a company with stable sales might find the moving average sufficient.
Hypothetical Scenario Demonstrating Improved Sales Forecasting Impact
Let’s consider a hypothetical scenario of a software company, “InnovateTech,” using CRM data to improve sales forecasting. Previously, InnovateTech relied on gut feeling and simple extrapolations from past sales. Their sales forecasts were often inaccurate, leading to misallocation of resources and budget overruns. After implementing CRM data analytics and using exponential smoothing, InnovateTech’s forecasting accuracy improved significantly. Their analysis revealed a strong correlation between the number of product demos conducted and subsequent sales.
This insight allowed them to allocate more resources to the sales development team, focusing on increasing the number of demos conducted. They also adjusted their budget, allocating more funds towards marketing campaigns targeted at high-potential customer segments identified through CRM data analysis. As a result, InnovateTech experienced a 15% increase in sales within the next quarter, exceeding their initial projections by 10%.
This success was directly attributable to improved forecasting accuracy, enabling more efficient resource allocation and strategic budget planning.
Optimizing Sales Processes Based on Data Insights
CRM data isn’t just for tracking sales; it’s a powerful tool for identifying and fixing inefficiencies in your sales process. By analyzing this data, sales managers can pinpoint bottlenecks, understand what works, and ultimately boost team productivity. This involves a systematic approach to examining various stages of the sales funnel and leveraging insights to improve overall efficiency.
Analyzing CRM data reveals hidden patterns and trends that often go unnoticed with traditional methods. For instance, a sudden drop in conversion rates at a specific stage of the sales cycle can highlight a problem area requiring immediate attention. Similarly, identifying which sales representatives consistently exceed targets and understanding their techniques allows for the replication of successful strategies across the team.
Pinpointing Inefficiencies in Sales Processes Using CRM Data
CRM data can illuminate various inefficiencies. For example, analyzing lead qualification reveals which sources produce high-quality leads and which are a waste of time and resources. Let’s say your CRM shows a high lead volume from social media ads, but a low conversion rate. This suggests a problem with your lead qualification process for those leads – perhaps the targeting is off, or the messaging isn’t resonating.
Similarly, analyzing follow-up procedures can identify delays or inconsistencies. If data shows a significant time lag between initial contact and the next follow-up, it indicates a need for improved process automation or better task management within the team. Analyzing average deal sizes associated with different lead sources can help prioritize high-value leads.
Identifying and Quantifying Effective Sales Strategies
CRM data allows sales managers to objectively measure the success of various sales strategies. For example, analyzing email campaign data (open rates, click-through rates, conversion rates) allows for A/B testing and optimization. If one email subject line consistently outperforms others, it indicates a more effective approach that can be replicated. Similarly, tracking the results of product demonstrations—quantifying the number of demos leading to closed deals—provides insight into the effectiveness of this sales strategy.
Analyzing sales representative performance alongside their usage of specific strategies (e.g., number of calls made, emails sent, demos conducted) allows for a deeper understanding of what drives success. For example, if representatives who frequently use video conferencing consistently close more deals, that strategy deserves more emphasis.
Actionable Steps for Optimizing Sales Processes
By analyzing CRM data, sales managers can proactively address weaknesses and implement strategies for improvement. The following table illustrates actionable steps based on common challenges:
| Process Area | Current Weakness | Improvement Strategy | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lead Qualification | High volume of unqualified leads | Implement a more rigorous lead scoring system based on demographics, behavior, and engagement | Reduced wasted time on unqualified leads, increased conversion rates |
| Follow-up Procedures | Inconsistent and delayed follow-ups | Automate follow-up emails and implement a CRM-based task management system | Improved response times, increased customer engagement, higher close rates |
| Sales Presentations | Low conversion rates after presentations | Analyze presentation content and delivery using CRM data to identify areas for improvement | More effective presentations, increased conversion rates |
| Sales Forecasting | Inaccurate sales forecasts | Use historical CRM data to build more accurate predictive models, incorporating factors like lead source and deal size | Improved sales forecasting accuracy, better resource allocation |
Enhancing Sales Team Training and Development with CRM Data

Unlocking the true potential of your sales team hinges on insightful, data-driven training. Your CRM system is a goldmine of information, ready to be tapped to refine training programs and boost overall sales performance. By analyzing CRM data, you can move beyond generic training and tailor development to address individual weaknesses and maximize strengths, resulting in a more effective and productive sales force.CRM data provides a powerful lens through which to examine sales team performance and identify areas ripe for improvement in training.
Analyzing key metrics reveals patterns and trends that point directly to skill gaps or knowledge deficiencies. This data-driven approach ensures training resources are allocated strategically, maximizing their impact and ROI.
Identifying Areas for Improvement in Sales Team Training Based on CRM Data
Performance data within the CRM, such as conversion rates, average deal size, and sales cycle length, can highlight specific areas where training is needed. For example, consistently low conversion rates at a particular stage of the sales funnel might indicate a need for enhanced training on objection handling or closing techniques. Similarly, prolonged sales cycles could suggest a deficiency in lead qualification or proposal development.
By correlating specific performance metrics with individual sales representatives, you can pinpoint training needs with precision. For instance, a representative consistently struggling with closing deals despite a high number of qualified leads would benefit from targeted training on closing strategies. Conversely, a rep with a high close rate but low average deal size may need training on upselling or cross-selling techniques.
Personalizing Training Programs Based on Individual Sales Representative Weaknesses
CRM data allows for personalized training plans tailored to individual sales representatives’ unique needs. By analyzing individual performance metrics, you can identify specific areas where each rep needs improvement. For example, a rep struggling with lead generation could receive focused training on prospecting techniques and social selling. Another rep might benefit from coaching on negotiation skills if their average deal size is consistently low.
This personalized approach ensures that training is relevant and effective, maximizing the return on investment in training initiatives. Imagine a scenario where one rep consistently loses deals at the proposal stage. CRM data could reveal this pattern, leading to personalized training focused on proposal writing, presentation skills, and value proposition articulation.
Tracking the Impact of Training Initiatives on Sales Team Productivity Using CRM Data
The effectiveness of training programs can be rigorously assessed using CRM data. By tracking key metrics before, during, and after training, you can quantify the impact of training initiatives on sales team productivity. For example, you can compare conversion rates, average deal size, and sales cycle length before and after a training program. A significant improvement in these metrics would indicate the success of the training.
This data-driven approach ensures accountability and allows for continuous improvement of training programs. Let’s say a sales team underwent training on a new sales methodology. By comparing their performance data before and after the training, measured through metrics like conversion rates and average deal size captured within the CRM, you can objectively evaluate the training’s effectiveness. A measurable increase in these metrics demonstrates a positive impact on sales productivity.